Are you at
risk?
The
biggest osteoporotic risk factor is simply being a woman. You are ten times
more prone to suffer from osteoporosis at an earlier age than your male
counterpart.
Osteoporosis
means, fragile bones, these bones break easily by slightest trauma. One in four women suffer from osteoporosis with increasing age after menopause
Women suffer
more
1) They have
an initial lower bone mass
2) Have a
higher bone loss with age particularly at menopause when oestrogen is decreased,
as they are the most important hormones in keeping the bone mass.
3) Women
live longer.
It is
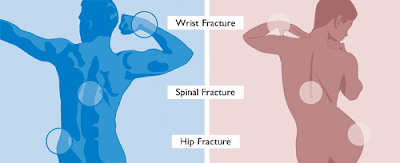
estimated that about 56% of women suffer from a fracture after the age of 60.These
fractures include spine, hip, wrist, ribs and upper arm. This makes life
difficult and painful.
Osteoporosis
is somewhat difficult to treat but easy to prevent. This prevention should
start early in childhood with good nutrition, plenty of milk and calcium as
this is required for bone formation, sports activities, and sunshine as this gives
us vitamin D. This should continue in adolescence. The maximum bone mass is
achieved in our late 20s to early 30s, after which it begins to decline.
Fractures are the main side effect of osteoporosis and they should be
prevented. However besides osteoporosis there are many other risk factors which
can cause fractures.
These
include:-
1) Being a
female
2) Age
3) Weight
and height
4) Parental
hip fracture at a young age
5) Smoking
6) Alcohol
7) Glucocorticoid
drugs
8) Antidepressants
called serotonin uptake inhibitors
For example- Prozac
9) Drugs for acidity called proton pump
inhibitors
10) Vitamin
D and K deficiency
11) Personal
history of soft trauma fracture
12) Rheumatoid
arthritis
13)
Ethnicity-(Caucasians have the highest risk for fractures.)
14) Premature
menopause
15) Lactose
intolerance and bowel problems
When we talk
about osteoporosis we always wonder how to make this diagnosis. There are many
tests to make this diagnosis, which I will talk about in the next few lines. However
it is clear from the above list that assessing the fracture risk is even more
important than making the diagnosis of osteoporosis. Many women have fractures
without osteoporosis. There are several
tools by which fracture risk assessments are done .The tools WHO: uses are called
FRAX, WHO does not always include BMD in their risk assessment. These tools
depend on local factors, such as facility for bone density, local economic
factors, reimbursement by insurance and people willing to pay for health issues.
There is no unified strategy to use. Basically if fracture risk is high, the individual is treated pronto, if intermediate do BMD and
reassess, if low follow the normal protocol. Bone is a living tissue it is
constantly being made and destroyed this keeps a balance. It is under the control
of many chemicals and hormones. It consist of a mesh if proteins called collagen
in which minerals are deposited mainly calcium. The tough outer wall of the
bone is called cortical bone; the inner tissue is called trabecular bone or
spongy bone or cancellous bone it is, porous and contains bone marrow,
produces blood cells.
 |
Normal Bone Osteoporotic Bone
|
It is this part of the bone that loses its minerals;
it is mainly calcium and becomes thin, thus causing osteoporosis. 99% of our body calcium is stored in our
bones. There are two types of cells involved in our constant bone remodelling.
They are called osteoblasts which form the bones and osteoclasts which destroy
the bone. A fine balance is maintained in this activity to keep the bones well tuned,
maintain body calcium levels, as this is very important for the activity of the
heart and muscles. As already mentioned this is controlled by various hormones
and chemicals in the body. Bone modelling and remodelling is done at the same
time. The bones are also sculpted. The maximum bone mass is achieved at around
the age of 30, after which it slowly starts to decrease. The adult skeleton is
replaced about every 10 years. The oestrogens keep the bone destroying cells
osteoclasts under control, and maintain the beneficial role of vitamin D.
So why does
osteoporosis happen?
Many of
these reasons overlap with fracture risks:
1) Oestrogen
deficiency in women which happens at menopause, testosterone deficiency in men
which happens with aging.
2) Under
activity of adrenal glands (a hormone producing gland in our body).
3) Under
activity of a hormone Calcitonin (produced by the Thyroid Gland)
4) Over
activity of another hormone called Parathyroid.This drains the calcium from the
bones.
5) Under
activity of the pituitary gland. This is the most important hormone producing
gland in our body. It is often called the band master of the body orchestra.
6) Prolonged
absence of periods which results in oestrogen deficiency caused by: anorexia
nervosa, excessive exercise ,high Prolactin level, a hormone which comes from
the Pituitary gland, surgical removal of ovaries or prolonged suppression of ovaries for medical treatment). All these
cause oestrogen deficiency
6)
Hypogonadism (poor functioning sex glands or may come from the poor activity of
the Pituitary ) again Oestrogen is depleted in women and likewise Testosterone
in men.
7) Brittle
bone disease (Osteogenesis imperfecta) .
This is a
genetic disorder where the bones are fragile due to defective collagen, and
break easily. It can be mild to severe.
8)
Malabsorption syndrome, chronic inflammatory bowel disease
9) Drugs,
corticosteroids, heparin, antidepressant and proton pump inhibitors (used for
acidity of the oesophagus and stomach)
10) Chronic
diseases, diabetes, renal, arthritis, liver, multiple myeloma, Systemic lupus
Erythematosus (these two are complex diseases) and HIV.
11) Prolonged
immobilization.
DIAGNOSIS OF
OSTEOPOROSIS AND FRACTURE RISK
The thoughts
on diagnosis of osteoporosis should start with a woman’s personal history and
risk factors which have been enumerated in the previous few lines for example
long term use of corticosteroids, smoking weight below BMI of 21. However X-rays
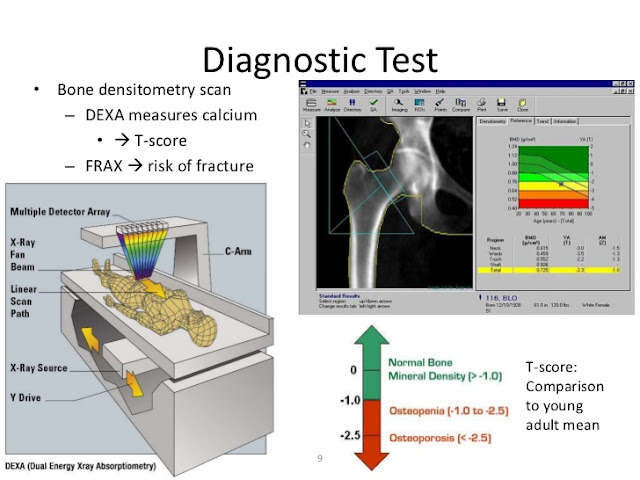
play a most important role in the gold diagnosis of osteoporosis. The best of
these tests is called DEXA; in simple words we can call it bone densitometry.
The test measures what is called BONE MINERAL DENSITY (BMD), it measures a
certain amount of minerals and tissues in a certain volume of bone (W/G/CM2). This
tells us if the bone is normal or a certain amount of bone is lost. This is
expressed on 2 measurements, T score, which compares it to a young white young
woman 30 years of age. The other is called Z score, which compares it to the
bone density in the same age group.
A T score of -1 is considered osteopenia, a T score
of -2.5 or below is considered
osteoporosis. This is an expensive test costing approximately $125 American dollars,
and also it is not available in many parts of the world, nor is it advocated routinely.
At the time of bone density assessment
you do not need any preparation you just lay on a machine with your clothes on,
the machine then scans your body, it takes about 15 minutes and reports are
calculated.
The fracture risk is expressed at the same time.
Different fracture risk tools are used in different countries. Bone density is
not always used to assess fracture risk.
Besides DEXA
scan, different types of x-ray studies are used, QCT, (quantitative computerised
axial tomography), ultrasound of the heel, plain lateral x-ray of the thoracolumbar region of the spine, this is often useful when we cannot do BMD.
Several
basic blood tests are required to exclude many other problems:-
1) Normal Full Blood Examination.
2) Hormones,
Thyroid, Parathyroid, Oestrogens, Pituitary and Testosterone in men.
3) Alkaline phosphatase,
Homocysteine a congenital problem in causation of osteoporosis.
4) Serum
calcium and vitamin D
5) Bone
turnover markers, are a recent tool which measure the end products of
osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity of bone in serum, blood or urine, which
gives us what is happening to the bones. These are rapid, reliable and cost
effective tests. One has to understand its biological analytical and
standardization process. At this stage these are very useful for fracture risk
assessment independent of B.M.D. In clinical practice it is useful to assess
the progress of people on osteoporosis treatment particularly those who are on a
given treatment to prevent bone reabsorption. One can also check on patients to
see if they are compliant to the treatment.
What is the
treatment of Osteoporosis and who should be treated with what?
Osteoporosis
(OP) is a silent disease; hence it is under treated in most countries of the world. The other problem is poor patient compliance
due to forgetfulness, side effects and not understanding the consequences of
the problem. We have to overcome these problems with education, good reminder
methods, minimizing the side effects or changing over to a drug more acceptable
to a woman. Prevention of OP starts in
childhood with good nutrition exercise and sunshine. This should continue at
all ages, a woman needs to take about 1000 to 1300 mg of calcium daily. Too much calcium can cause some cardiac problems;
hence there is some international debate on this issue. This should be
accompanied by 800 international units of Vitamin D (1 microgram of Vitamin D
is = to 40 INU); this can be taken as a lump sum once a month. One of the main
roles of Vitamin D is to absorb calcium from the gut, allowing calcium and
phosphorus levels to control bone formation. It also keeps the parathyroid
gland under control. Sunshine for a few minutes in summer is adequate to make
up your Vitamin D, may be a short walk at lunch time, prolonged sun exposure
does not keep increasing your vitamin D; however it increases your risk of skin
cancer. If the UV index is more than 3, sun exposure should be avoided. This is
to prevent the risk of skin cancer.
Lifestyle
factors should be improved, such as; stop
smoking, limit alcohol intake, along with soft drinks, tea,
coffee and sugar. Try and decrease your weight, if you are very overweight and
see if some of the drugs you take for other diseases can be readjusted. Some
studies have shown a role of vitamin K, but at this stage it is not recommended
for the treatment of OP.
Pharmacological
treatment is recommended in almost all pre and post menopausal women under the
age of 60. Initially they were prescribed a drug called PROFOX (a combination
Prozac and Fosamax) which in my opinion was no good. Fosamax has its own
side effects and Prozac is no good for OP. In the first 5 years of menopause
not only do women lose 1% of their bone density, they lose collagen from the
skin thus losing its thickness, losing intervertebral discs which make one fifth
of the length of the spine, there are emotional changes due to lack of oestrogens,
at times of life cycle as postpartum, premenstrual, so in my view hormone
replacement treatment will be the best treatment before the age of sixty. It
will take care of all other symptoms for example: hot flushes, poor sleep,
depression and all that goes with menopause and prevent losing bone. Many
clinicians are reluctant to use HRT because they have not familiarised
themselves with its use. Depending on if the woman has a uterus she can have
oestrogens and progesterone, otherwise if she has no uterus oestrogens alone do
very well. Many different types of oestrogens and progesterone can be taken by
different routes to prevent side effects. They decrease risk of hip and spinal fracture,
bowel cancer, heart attacks and mortality. After 5 years of treatment bone
density has been shown to rise by about 10 %. The only risk is a very small
risk of increase in breast cancer. The Thromboembolic risk (Thrombus) can be
managed by using Transdermal (on the skin) oestrogens. The breast tenderness
and vaginal bleeding problems are easily managed.
Bisphosphonates
is the main group of drugs used by most clinicians as the first line of
treatment.
Who should
be given these drugs?
1) Those that
have had a minimum trauma fracture have a high fracture risk with or without
using BMD
2) Those
with a T score of -2.5 or lower.
3) On high
doses of corticosteroid for more than 3 months
4) High risk
factors for OP
Various Bisphosphonates
Alendronate:
70 mg orally once weekly. On the
remaining 6 days women can take vitamin D and calcium in the usual dosage
The other
Bisphosphonate often used is Risedronate: 35 mg orally once a week or 150 mg
once a month.
Ibandronate:
150mg orally once a month or it can be given 3 mg IV every 3 months.
Zoledronic acid
(another Bisphosphonate) is given
5 mg in
100mls IV slowly once a year.
Bisphosphonates
are advised to be taken on an empty stomach first thing in the morning with a
glass of water, after that keep standing, do not eat or drink anything else. Bisphosphonates
attach to the surface of the bone thus slowing the activity of osteoclast cells.
Bisphosphonates have many serious side effects. The main side effect of these
is gastric upset and esophageal burning, nausea, vomiting, joint and muscle
pains, fever, loosing of teeth, jaw pain, constipation and fatigue. One of the
two very rare complications quoted are osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical
fracture of the femur. These usually, only happen if they are used in very high
doses for bone cancer. There is no definitive date as to how long this therapy
should be used. No therapy is indefinite, after 1-3 years or if there is another
fracture it should be reassessed. It is believed that the benefit of Bisphosphonate
treatment can last up to 5-10 years, however it is worth while repeating BMD ,
BTM , and fracture risk after 1-3 years.
During this time calcium and vitamin D should be continued. Combination
therapy with other drugs does not provide any benefit.
Denosumab,
is the latest achievement in the treatment of osteoporosis. It is used as a
first line of treatment in some countries. It is a monoclonal antibody (like a
vaccine) and attacks only one type of cell. It works by disabling the
maturation and activity of osteoclasts, and the only problem is that its effect
does not last when the drug is stopped. Before starting Denosumab assess the
oral cavity to decrease the risk of osteonecrosis of jaw (this is very rare),
and make sure there is no hypocalcaemia. There is some concern about its effect
on the immune system (increased risk of infections) and its use after bisphosphonates,
on the bone after treatment is stopped. The dose of Denosumab is 60 mg in 1ml given
every 6 months subcutaneously, (meaning under the skin). It can cause side
effects like any other drug and you can get this list from your caregiver. A 5
year trial with Denosumab has been very successful. Its use decreased the risk
of spinal fractures by 70%, hip fractures by 40%. It does not have a cancer risk.
The cap on the syringe is latex so let your caregiver know, that you have a
latex allergy. There is a special programme called Provital, which can keep
reminding you when your next treatment is due.
The other
very simple treatment for OP is Raloxifene. This is a special oestrogen which
has different actions in different organs, hence effective with bones; it does
not cause breast cancer. The dose is 60 mg daily, taken orally and you do not
have to fast. It should not be given to people who have a history of deep
venous thrombosis or have been immobilised for a long time.
Teriparatide:
Is a synthetic form of Parathyroid hormone and acts by decreasing bone
resorption and improves bone formation. 20 micrograms are given daily by
subcutaneous injection. Its use is restricted to 18 months as its long term use
caused bone cancer in animals. It is recommended that it is followed by
Bisphosphonates.
Abaloparatide is the latest drug that is being used in place of Teriparatide.
It is
recommended that any treatment is followed every 1, 3, 5 years depending on the
individual situation. Treatment should be offered for various disorders, which
cause secondary osteoporosis.
There are many new drugs and treatments now available in different situations.
So much on
osteoporosis why is it such a significant problem? Life
expectancy is increasing hence the risk of osteoporosis is increasing. There
are almost 200 million women in the world who have osteoporosis, may be many
more about whom we do not know. There are 8.9 million known fractures caused in
the world annually. It costs 70 -20 billion US dollars to treat them. Do not
forget that in most parts of the world many are never treated. It was estimated
that a fracture occurs in the world every 3 seconds. Osteoporosis is a silent
disease, it causes untold problems to the individuals, pain, disability, poor
quality of life, and death, too much cost to the nations, too much cost to the
world. The good news is that health providers and the public are both becoming
aware about it, so let us start with education, information and prevention. The
new technologies are providing us with better and better treatments. Even
surgery is used for correction of spinal defects caused by osteoporosis. The
main prevention should start in childhood, good nutrition sunshine and
exercise. Later focus on lifestyle factors, nutrition, calcium, vitamin D
measures for fall prevention,(do not walk in the dark or cluttered spaces, be
aware of the drugs that can cause dizziness), exercise and regular medical
advice on your health. Do not ignore the treatment that is offered to you.


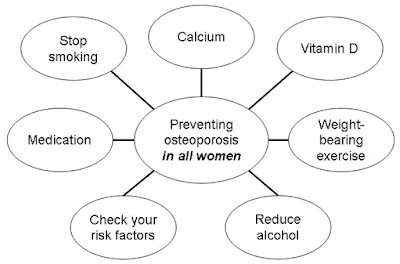
KEY POINTS:-
Start prevention early in life rather than later.
Regular exercise.
Good Nutrition.
Sunshine.
Vitamin D and Calcium.
Stop Smoking
Limited Alcohol